You can explore our project materials through the GitHub repository and our detailed project report.
The ClustVarSelect package represents a significant advancement in feature selection for high-dimensional biological data analysis. Our implementation combines power k-means clustering with Bregman divergences and sparse manifold decomposition (SMD) to identify discriminative features in single-cell RNA sequencing data. The package offers improved clustering robustness through adaptive annealing schemes and supports multiple data formats commonly used in bioinformatics workflows.
Key innovations include:
Integration of power k-means with various Bregman divergences (Euclidean, KL, Itakura-Saito, logistic) for outlier resilience
Entropy-based (decision trees) and maximum margin (SVM) classification
Efficient parallel processing for large-scale datasets
Compatibility with sparse matrices, SingleCellExperiment, and Seurat objects
Comprehensive visualization and analysis tools
Key Results
Synthetic Data Performance
Testing on synthetic datasets with varying sample sizes, feature counts, cluster numbers, and noise levels demonstrated that our Bregman power K-means implementation consistently outperformed regular K-means clustering. The improvement was particularly notable when dealing with:
Increased cluster numbers
Higher noise levels
Greater outlier proportions
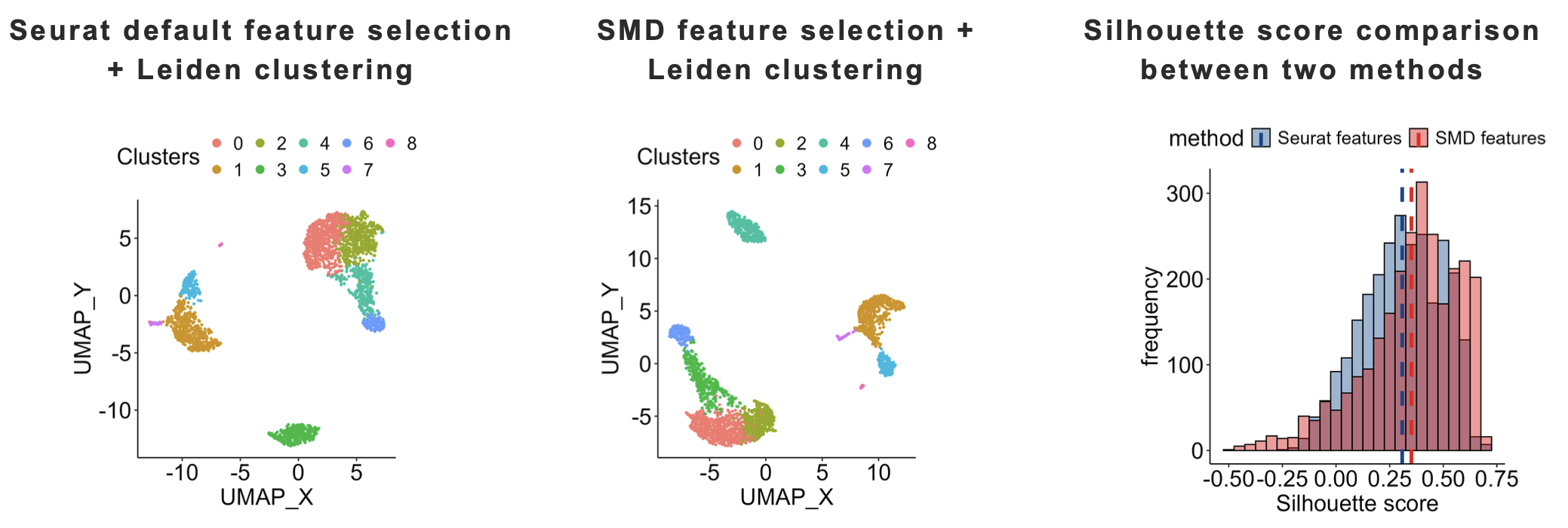
PBMC-3K Dataset Analysis
On the gold-standard PBMC-3K dataset, our implementation showed several key advantages:
Improved Clustering: The Bregman power K-means produced clustering results more consistent with Seurat’s established output compared to regular K-means.
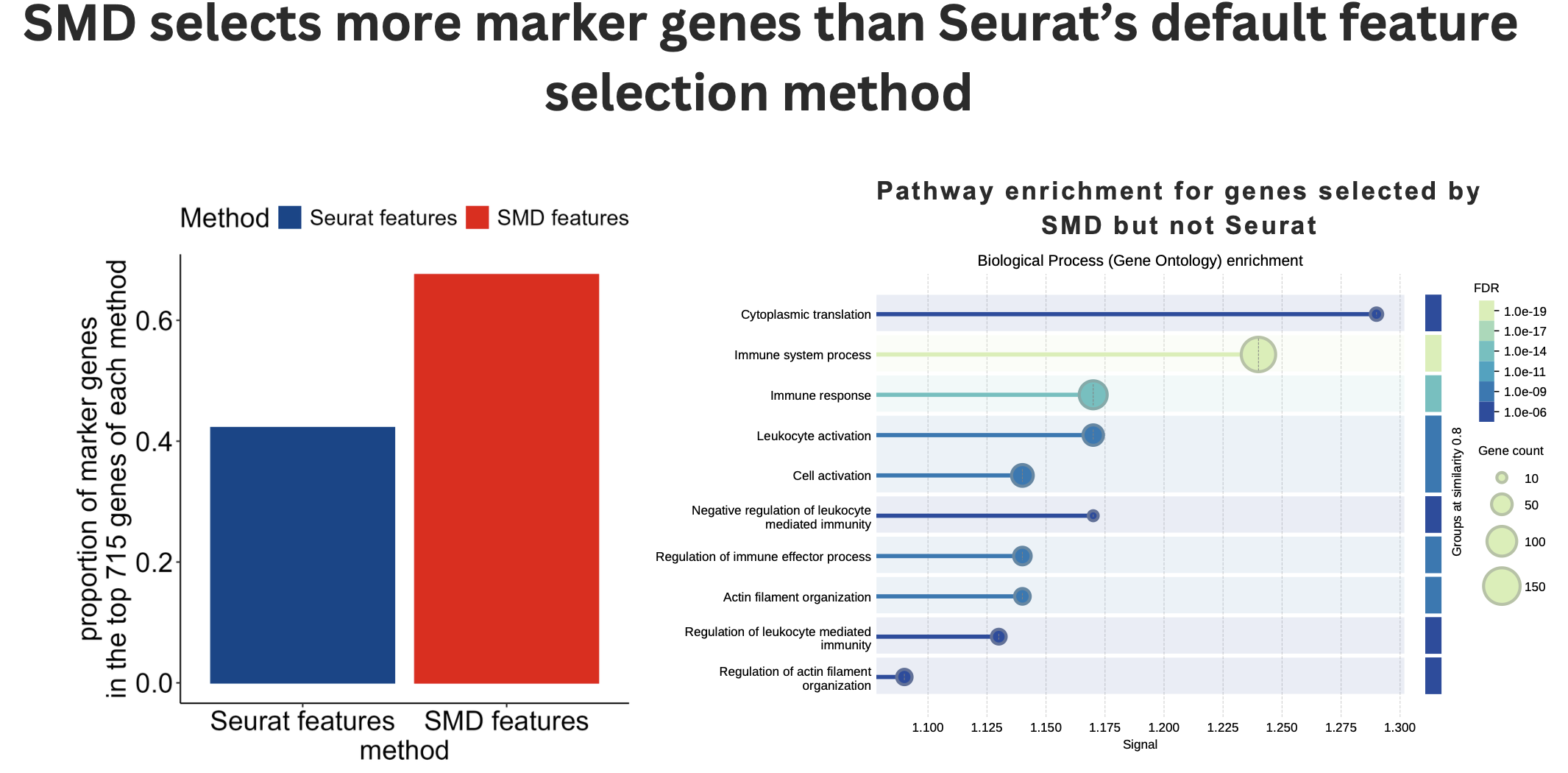
Enhanced Feature Selection: The SMD algorithm selected more marker genes than Seurat’s standard approach, demonstrating superior biological relevance.
Biological Significance: Pathway enrichment analysis of SMD-selected features revealed meaningful immune pathways, aligning with the expected biology of peripheral blood samples.
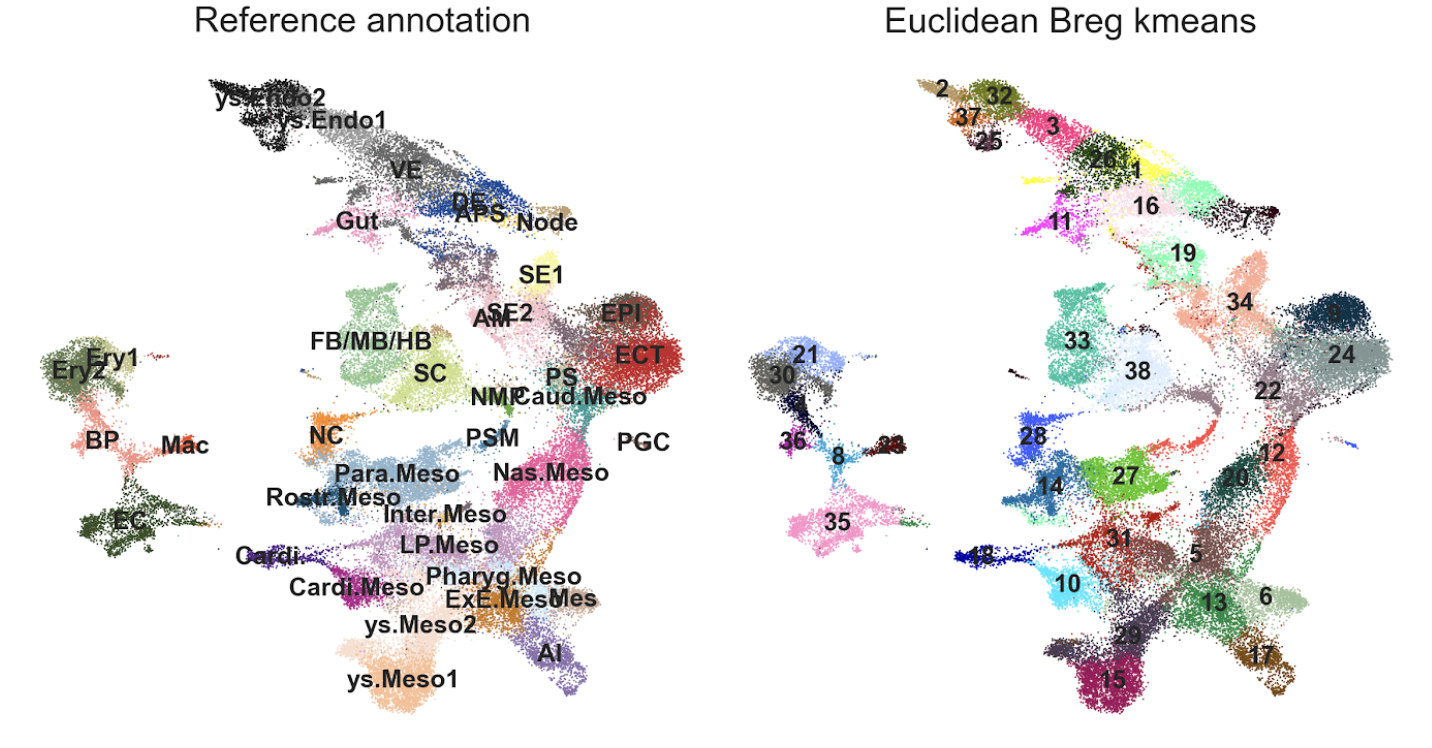
Large-Scale Application
Testing on a monkey single-cell atlas (56,636 cells across three developmental stages) revealed:
The Euclidean version of Bregman power k-means successfully identified major cell types
Processing time was approximately 3 minutes for this large dataset
While effective for clustering, the SMD component showed computational scaling challenges with larger datasets
This project was developed in collaboration with Zhiyuan Yu and Adrian Con Garcia, combining expertise in computational biology, statistical methods, and software development to create a robust tool for modern single-cell analysis.